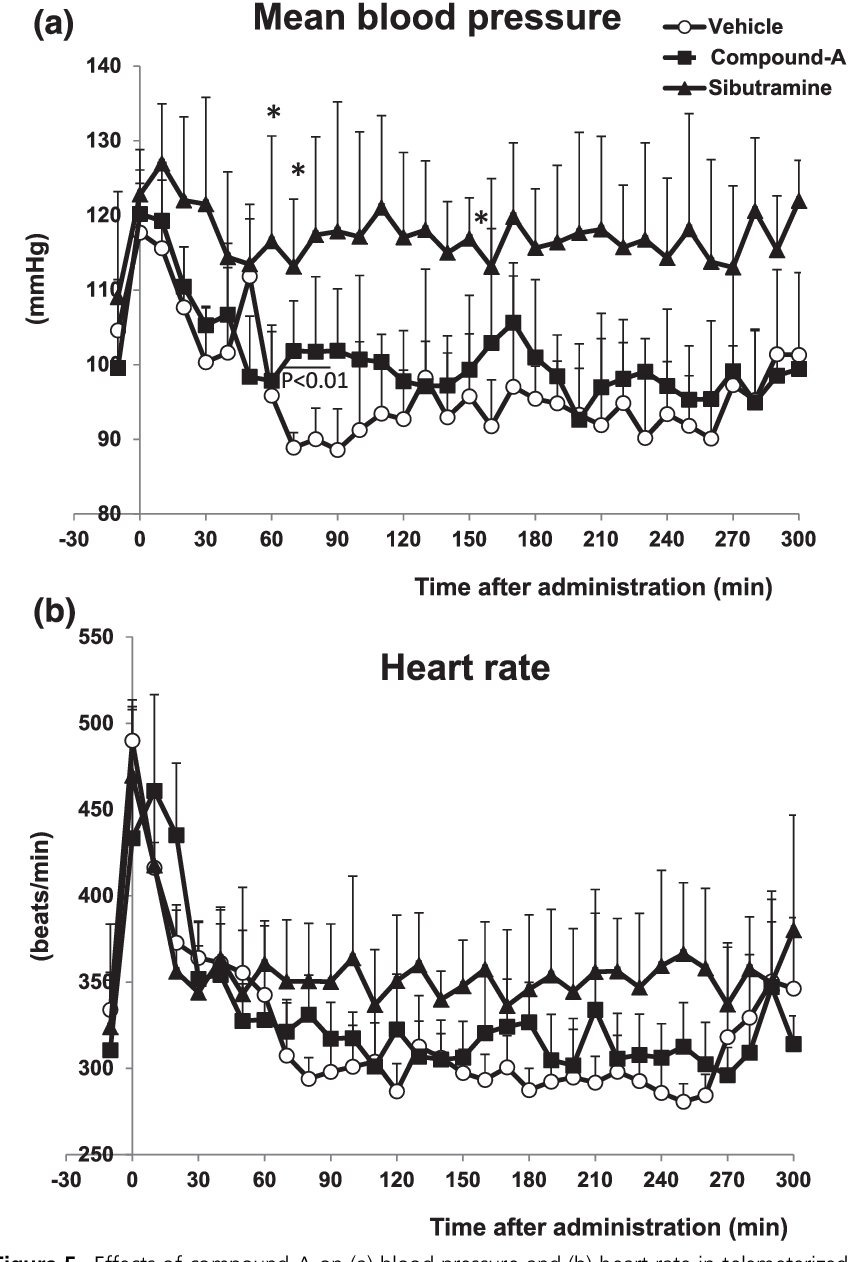
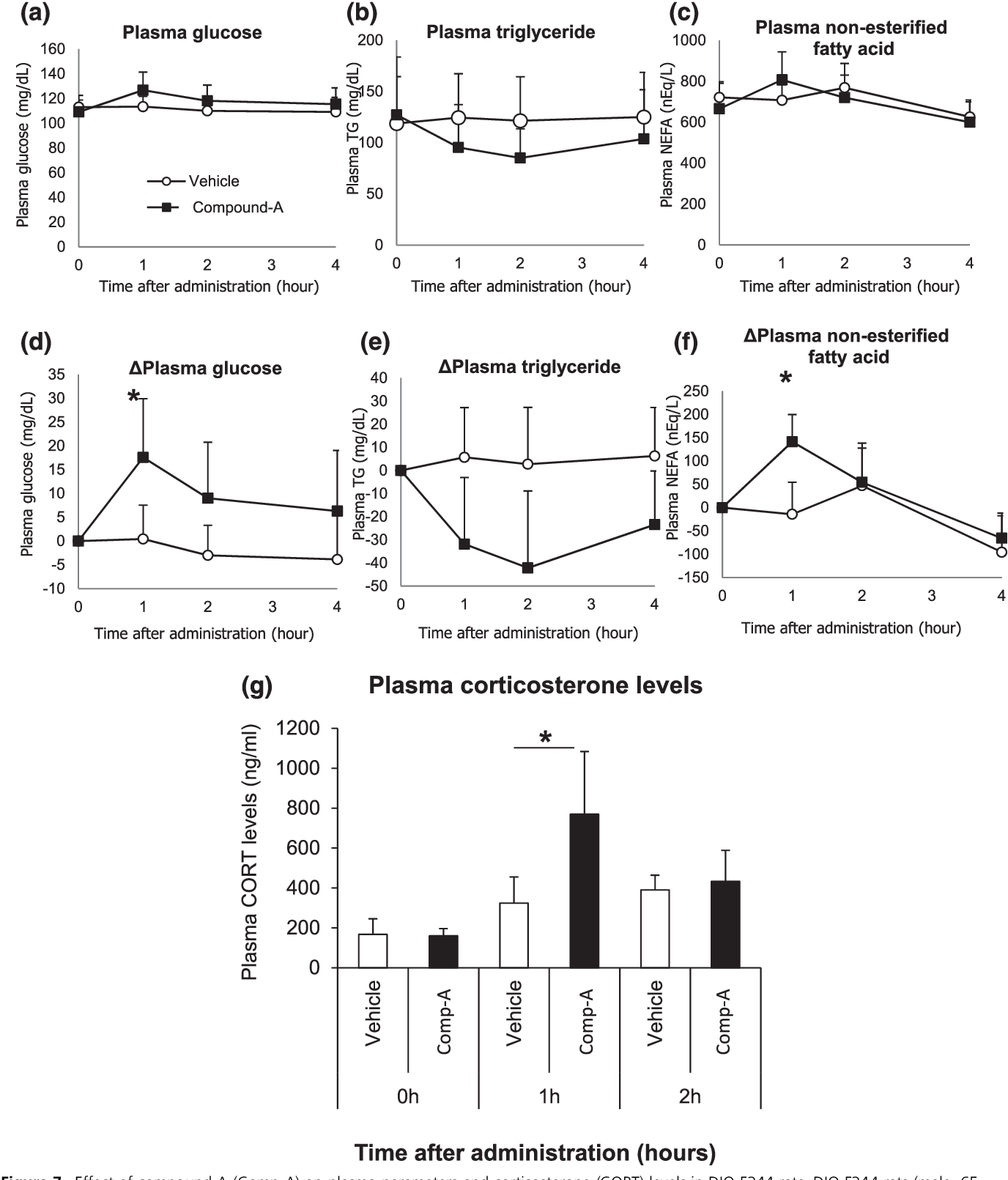
The bombesin receptor subtype 3 also known as BRS-3 or BB3 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BRS3 gene.
Function
Mammalian bombesin-like peptides are widely distributed in the central nervous system as well as in the gastrointestinal tract, where they modulate smooth-muscle contraction, exocrine and endocrine processes, metabolism, and behavior. They bind to G protein-coupled receptors on the cell surface to elicit their effects. Bombesin-like peptide receptors include gastrin-releasing peptide receptor, neuromedin B receptor, and bombesin-like receptor-3 (BRS3; this article).
BB3 is a G protein-coupled receptor. BB3 only interacts with known naturally occurring bombesin-related peptides with low affinity and therefore, as it has no natural high-affinity ligand, is classified as an orphan receptor.
References
Further reading
External links
- "Bombesin Receptors: BB3". IUPHAR Database of Receptors and Ion Channels. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2007-10-25.
- bombesin receptor subtype 3 at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Human BRS3 genome location and BRS3 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.